The second part of an article by Scot.E3 activist Brian Parkin which was first published on the rs21 website on August 18, 2023. It (and the first part) provides useful background for the discussion on nuclear power that took place on October 18 2025 at the Scot.E3 conference.
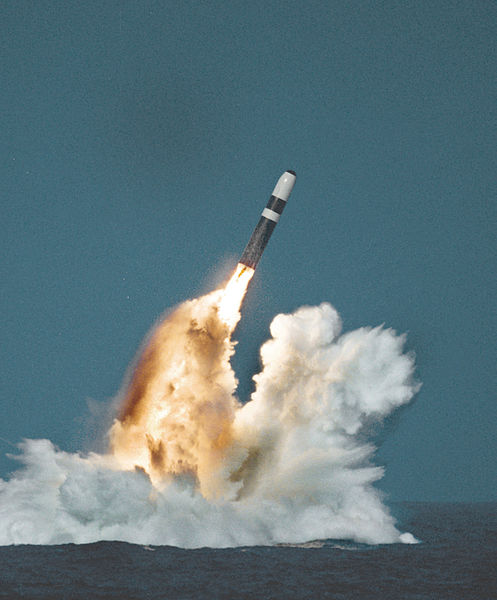

In the first part of this short series, Brian Parkin showed how Britain’s nuclear power programme was a consequence of a nuclear weapons project intended to maintain Britain as a top flight imperialist nation. Here he explains how the ideological delusions and military secrecy that this generated has left Britain with one of the most uneconomic and unreliable power generation liabilities on the planet.
British governments after 1945 pursued a consensus of national recovery based on the re-energising of a depleted economy via new technologies and a welfare state social contract, to drive up productivity and profits to a level capable of sustaining Britain as a world power.
But the post-war ‘spheres of influences agreement’ of 1945 between the USA, Russia and Britain rapidly gave way to the Cold War and a new arms race. The Cold War divided the world into two armed camps, and with the formation of NATO in 1949, much of western Europe fell under the leadership of the USA against the Soviet Union and its Warsaw Pact allies. A year later, with the outbreak of the Korean War, it became clear that sections of the US military were lobbying for the use of nuclear weapons as first strike options.
What was clear within this new order was that Britain’s sphere of influence had dissipated into that marked out by the US nuclear super-power. But Britain nevertheless persisted with its own atomic bomb programme, as well as a V bomber programme as the means of delivering it. For Britain’s cold warriors, this was central to a military first-strike nuclear capacity which would keep them on a par with the USA. As the armed forces Chiefs of Staff Committee put it: ‘If we did not develop megaton weapons (hydrogen bombs), we would sacrifice immediately, and in perpetuity, our status as a first-class power’
Imperialism, independence and isotopes
This ambition was under-written by a total of six Magnox reactors – two at Calder Hall (now Sellafield) and four at Chapelcross in Dumfries – which were central to western plutonium production for H-bombs. By 1958 these reactors had a total capacity of 250 Mw of electrical output. But like the commercial Magnox stations to follow, these reactors proved at times to be unreliable, and the technology posed dangerous challenges. And while Britain was a useful source of cheap plutonium, the USA harboured doubts regarding Britain’s ability to sustain both the empire and a first strike nuclear capability.
Then in 1958, the first British H-bomb test took place on Christmas Island in the Pacific. This was followed by an amendment of the US-UK Mutual Defence Agreement, mainly as a means of controlling British nuclear activity by limiting its share of targets within USSR airspace. For a while the plutonium deal with the US remained a one-way street, until UK nuclear strategy became based almost entirely on H-bombs. This now meant the Britain becoming dependent on the US for its supply of tritium (an isotope of hydrogen) necessary for completing the reaction implosion, and thereby boosting the nuclear yield. This was the first stage in the unravelling of the myth of Britain’s ‘independent’ nuclear weapons.
Perhaps the most farcical aspect of the nuclear ‘special relationship’ was the complete American control over Operation Blue Danube – the joint USA-UK European nuclear attack plan. This gave the USA the power of veto over any first strike by the RAF. Overall American command of Nuclear Forces Europe meant that all nuclear weapons, even those at RAF V bomber bases, were in practice American property. All nuclear weapons manuals, fuses, fuse locks and fuse codes were kept in a secure vault on the RAF base, and the agreement provided that ‘…in the event of any RAF personnel attempting to obtain any secured items without superior and strategic authorisation, the [American] marine guards should exercise the duty to shoot (him/her/them) dead’.
Uncritical accountancy
Following the successful production of plutonium from the initial Magnox reactors, the Labour governments of the 1960s decided to proceed with a large-scale civil nuclear power programme. Any doubts regarding the costs of this venture were set aside by the strategic ‘need’ for plutonium, and the belief in nuclear power as protection against a possible miners’ strike. Given such strategic values, even the most basic cost-benefit analysis was regarded as wholly unnecessary.
But in 1988 all of the UK’s nuclear power secrets fell onto the desks of the National Union of Mineworkers Research Department, with the performance and costs of every reactor revealed. They showed that Magnox units constructed under ‘even under the most favourable and lowest Treasury discount (interest) rates, had at best performed at twice the cost of coal-fired stations’. They were hopelessly inefficient, in large part due to inherent design flaws such as fuel-rod alloys with a tendency to react explosively on contact with water, and graphite cores which could start to burn at high reactor temperatures. For these reasons, Magnox stations had never run at full capacity.
The figures were even more dismal for the second generation of Advanced Gas (cooled) Reactors (AGRs). Intended to run continually while being re-fuelled, these reactors experienced both fuel rod and control rod jamming. Steam temperatures were rarely optimal and heat exchangers often over-heated. These flaws combined to make them impossible to run at anything like full capacity, with utilisation sometimes as low as 18%. EDF, which would later take them over for almost nothing, described them as ‘basket cases’. One Treasury official in the run-up to electricity privatisation described them as ‘…the most expensive engineering folly ever under-written by the UK taxpayer’.
The dog and the lamp-post: the US-UK special relationship
The super-power dreams embodied in the V bombers had quickly foundered on Russian advances in air defence. With the shooting down of a US spy-plane high over central Russia in 1960, it was clear that no RAF plane with atom-bombs was going to reach its target. In a way this suited some American strategic thinking, as shown by a White House directive of April 1961 which called for a ‘downgrading’ of the ‘special relationship’ and for ‘forcing a greater UK integration into Europe’.
This allied integration could best be hurried by ‘not prolonging the UK bomber force’– a task quickly achieved through the American failure to complete air-launched missiles upon which the RAF pinned its future strategic role: first Bluestreak (abandoned in 1960) and then the Skybolt (scrapped 1961). But the US was sensitive regarding ‘The UK’s loss of prestige and self-esteem’, hence the sop to share in its Polaris nuclear submarine deterrent, by basing the American vessels at Holy Loch, just 25 miles from Glasgow.
Privatising Prometheus
The eventual privatisation of the UK electricity industry went ahead in 1990, but only on the basis of the government footing the bill for untold nuclear liabilities, and the power stations themselves being split between two companies: Magnox Ltd, a wholly government operation set up prior to the oldest stations being handed over to a Nuclear Decommissioning Agency; and EDF, which acquired the AGRs for a notional peppercorn price, and was also allowed to operate its own power sales company.
The British nuclear power project arose from what was essentially an imperialist H-bomb imperative. As such, it escaped any public economic scrutiny. Instead, it became a key component of the post-1945 great British super-power illusion. Failures in the Magnox reactors were denied because their main job was to produce plutonium for the British nuclear ‘deterrent’. That same arrogant disregard of accountability and high secrecy still marks the nuclear power project to this day.
And now of the AGR fleet, only Heysham 2, Hartlepool and Torness remain in operation, up to 2028, at which point the highly subsidised Pressurised Water Reactor at Sizewell B (the only one ever built in Britain) will be the only pre-privatisation nuclear station left running. When they close, the costs of decommissioning will fall to the tax-payer, a bill that may well run into the next century. But we can be certain of one thing: the plutonium breeding reliabilities of Calder Hall, Chapelcross and the undisclosed number of ‘civil’ Magnox’s. Because somewhere at the leaking, creaking and decaying Sellafield complex, there are 139 metric tonnes of the deadliest material known to humankind with a half-life of 82 million years.